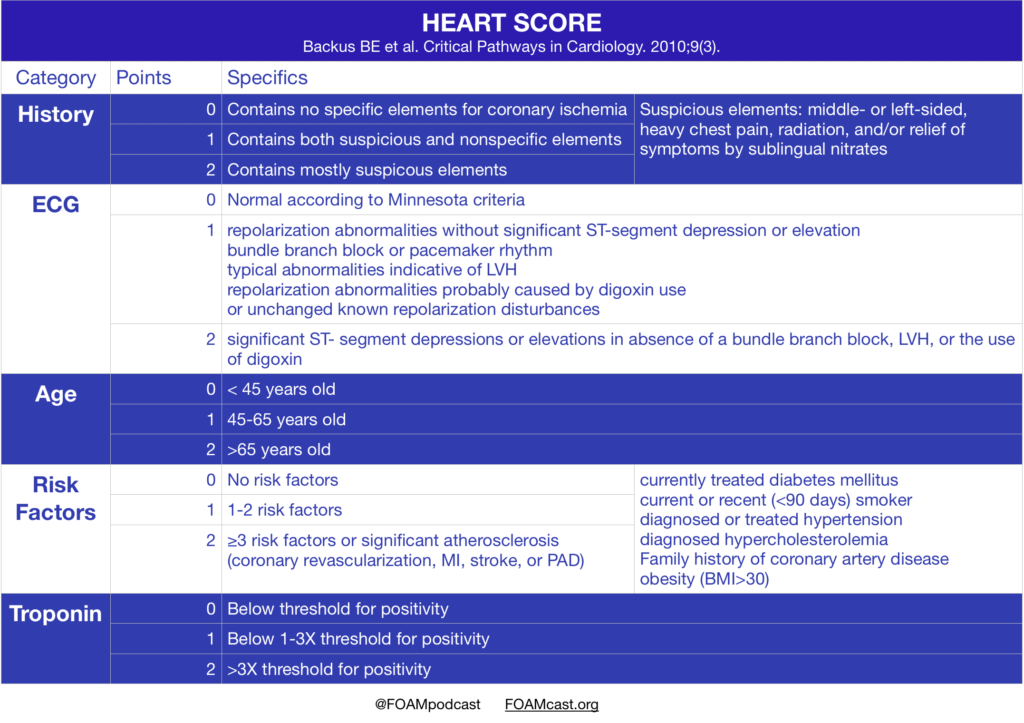
We cover the clinical policy from the American College of Emergency Physicians – Clinical Policy: Critical Issues in the Evaluation and Management of Emergency Department Patients With Suspected Non–ST-Elevation Acute Coronary Syndromes
Check out our sponsor for this show, Figure 1, a free open access application for providers using images and cases.
Rosh Review Emergency Board Review Questions
An elderly man presents with 4 episodes of angina in the past 24 hours. His medical history includes diabetes and asthma. Based on initial testing, you diagnose non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction. You are waiting for the cardiac team to admit him to the critical care unit. In the interim, which of the following is the most appropriate medication to begin?
A. Atelplase
B. Clopidogrel
C. Digoxin
D. Metoprolol
[accordion]
[toggle title=”Answer” state=”closed”]
B. Non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) treatment begins with a basic anti-ischemic regimen consisting of oxygen, morphine, nitrates, and possibly beta-blockers and ACE-inhibitors. Antiplatelet medications are then considered. Choices include aspirin, clopidogrel, and prasugrel. NSTEMI treatment is rounded out with anticoagulants such as enoxaparin, bivalirudin, and fondaparinux. Based on risk stratification, definitive treatment may include medications-alone, angiography, percutaneous cardiac intervention or coronary artery bypass surgery. Clopidogrel acts by irreversibly inhibiting a platelet receptor that is needed for activation, thereby inhibiting platelet function. Thrombolytics (fibrinolytics), such as alteplase (A), reteplase and tenecteplase, are contraindicated in the treatment of NSTEMI, as they have shown worse outcomes with their use. Digoxin (C), a cardiac glycoside, is used in treating certain dysrhythmias and heart failure, not myocardial infarction. Beta-blockers such as metoprolol (D) carry a relative contraindication in patients with severe COPD, asthma, atrioventricular block, hypotension or bradycardia.
[/toggle]
[/accordion]