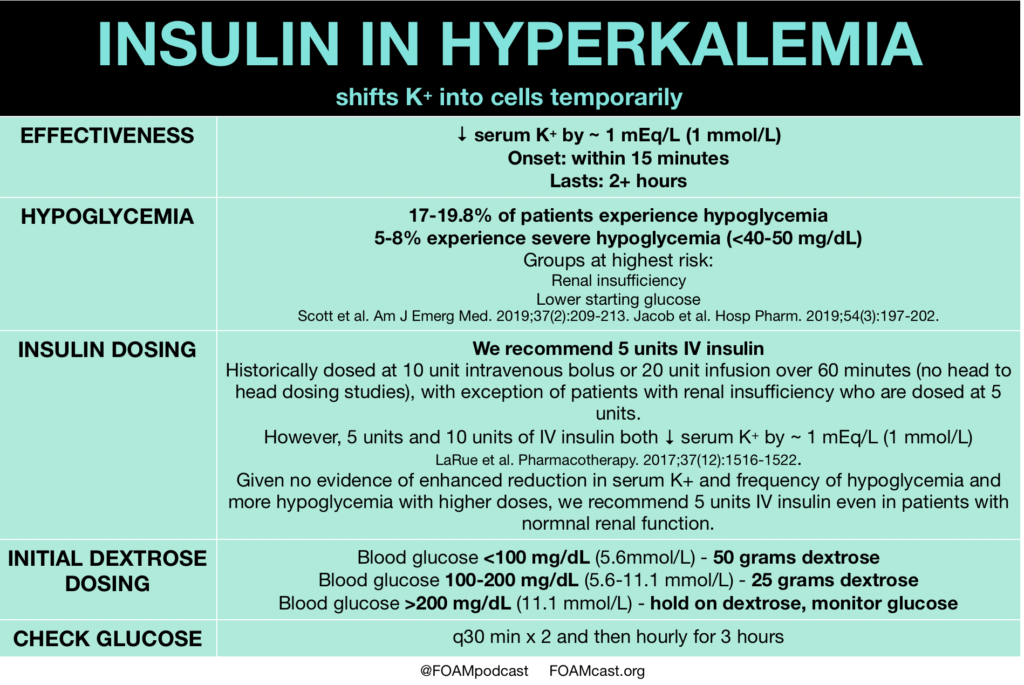
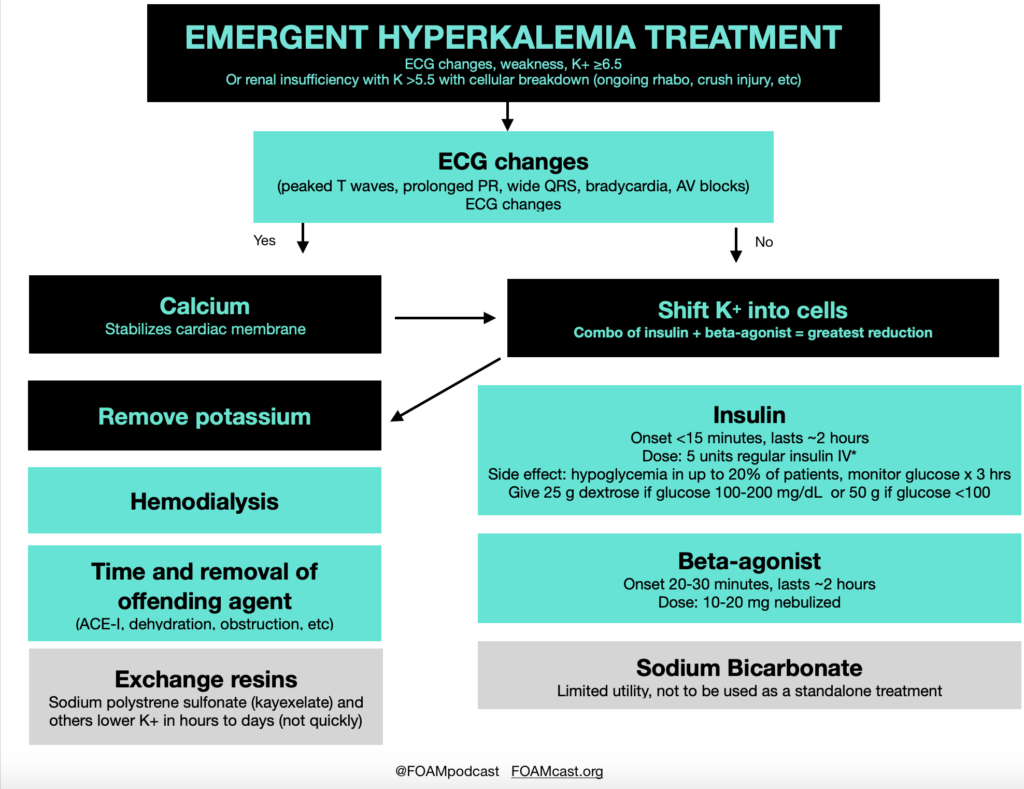
Insulin is a mainstay in the emergent treatment of hyperkalemia but comes at the cost of increased risk of hypoglycemia, which is quite common.
References:
- Scott NL, Klein LR, Cales E, Driver BE. Hypoglycemia as a complication of intravenous insulin to treat hyperkalemia in the emergency department. Am J Emerg Med. 2019;37(2):209-213.
- Apel J, Reutrakul S, Baldwin D. Hypoglycemia in the treatment of hyperkalemia with insulin in patients with end-stage renal disease. Clin Kidney J. 2014;7(3):248-50.
- Coca A, Valencia AL, Bustamante J, Mendiluce A, Floege J. Hypoglycemia following intravenous insulin plus glucose for hyperkalemia in patients with impaired renal function. PLoS ONE. 2017;12(2):e0172961.
- Larue HA, Peksa GD, Shah SC. A Comparison of Insulin Doses for the Treatment of Hyperkalemia in Patients with Renal Insufficiency. Pharmacotherapy. 2017;37(12):1516-1522.
- Jacob BC, Peasah SK, Chan HL, Niculas D, Shogbonnwaesei A. Hypoglycemia Associated With Insulin Use During Treatment of Hyperkalemia Among Emergency Department Patients. Hosp Pharm. 2019;54(3):197-202.
- Harel Z, Kamel KS. Optimal Dose and Method of Administration of Intravenous Insulin in the Management of Emergency Hyperkalemia: A Systematic Review. PLoS ONE. 2016;11(5):e0154963.
- Pierce DA, Russell G, Pirkle JL. Incidence of Hypoglycemia in Patients With Low eGFR Treated With Insulin and Dextrose for Hyperkalemia. Ann Pharmacother. 2015;49(12):1322-6.